How do I register a new hotspot?
If you don’t have a HOTSPLOTS account yet, you’ll have to register with us first. Under “My hotspots” in the registered users section you will find the following form which lets you register a new hotspot under your account:
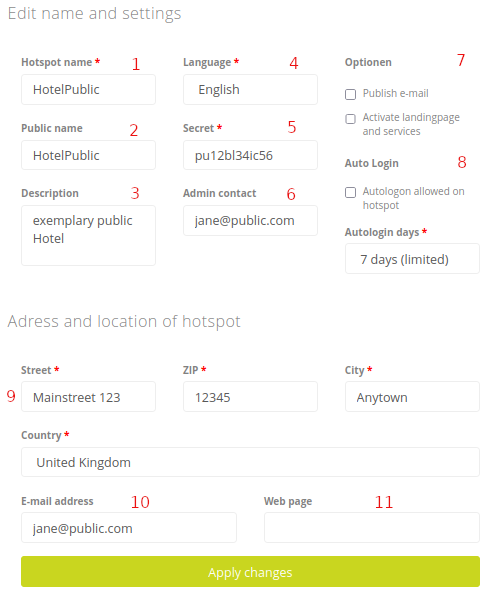
The fields have the following meaning:
- Hotspot name: The name identifies the hotspot in our database and should be as clear as possible. This name must not contain special characters or spaces.
- Public name: Since neither spaces nor umlauts are allowed in the hotspot name, there is also the public name. If nothing is entered, the hotspot name is used instead. All users will see this name on the login page of your hotspot: Welcome to the hotspot “HotelMuster”. On our map this name is also used (except for hotspots with rate “V.I.P. / Nur Tickets”).
- Description: Here you can add any descriptive text that hotspot seekers will see in our database.
- Language: currently Arabic, Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Dutch, English, German, French, Greek, Italian, Polish, Romanian, Russian, Spanish, Ukrainian are available. This setting is used as default for the login page of this hotspot. The user can change it there for him-/herself.
- Secret: The secret is a key that the hotspot router uses to log on to our server. You must also store the key that you enter here on the hotspot router. So choose a character string that is as random as possible. You can choose the key yourself.
- Admin contact: You can enter several e‑mail addresses, separated by spaces, to which e‑mails are automatically sent by the monitoring system if the hotspot is offline for the time specified under failure reports.
- Options: In the following checkboxes, choose whether you:
- Release your e-mail address. If you share your e‑mail address, it will be displayed as the contact address for the hotspot. This can be useful if surfers have questions about your offer or problems arise.
- enable the landing page as a service. We would be happy to advise you on additional services and the landing page designed individually for you. Please contact us for more information, we will find an optimal solution together with you.
- Auto login: After a connection to the hotspot has been established, there is the option of automatically reconnecting. Devices with a known MAC address are automatically logged in. The MAC addresses are saved after a login for the specified time.
- Street, zip code, city, country: Enter the location of your hotspot here. The default address is the one you used to register with us. This information is helpful so that other users can find your hotspot in our database.
In a first step, we use the zip code to determine the geographic position of your hotspot and to display it on our map. You can then precisely adjust the position on the map. - E-mail address: Enter an e-mail address for the hotspot here. This can be displayed as a contact address for users if desired (“release e-mail address”).
- Web page: You can enter a URL for each of your hotspots, which will be displayed on our overview map. So you can e.g. B. Make your hotel’s homepage public.
Then click on the green “Apply changes” button to register the hotspot with us. You can delete it again at any time or change its data by clicking on its name in your hotspot list:
You can also customize the login page of your hotspot if you e.g. B. want to display a picture of your hotel or an individual greeting.
What do I need to run a hotspot?
To run a hotspot, you need two things:
Preferably a DSL connection:
A DSL connection with a flat rate provides a fast connection to the internet. Depending on the location, alternatives to DSL can also be used to connect to the internet.
A WiFi router:
Users can use it to connect to the wireless network. At the same time, it monitors who is using the internet. Only those who can authenticate themselves via HOTSPLOTS are forwarded to the internet. And you as the operator will regularly receive your share of the revenue.
Here you will find an overview of our current products.
We would also be happy to advise you personally and respond to your needs when choosing our products. Use our contact here.
Here you will find an overview of our current products.
We would also be happy to advise you personally and respond to your needs when choosing our products. Use our contact here.
Which WiFi routers are suitable for HOTSPLOTS?
We recommend the routers from our webshop as hotspot routers. For outdoor WiFi installations we recommend the devices from Ubiquiti.
All hotspot routers can also be used as access points or repeaters. All devices with the same firmware generation can be connected to each other as repeaters. Repeaters with firmware 2.0 can work but cannot be connected to newer access points or routers via radio – but the other way around.
Our firmware offers the following advantages, among others:
- The hotspot can be managed easily with a web browser
- VPN routing as protection for hotspot operators
- Monitoring system: If the hotspot router is no longer online, the HOTSPLOTS server automatically sends a failure message by e-mail as well as a message when the malfunction is resolved.
- Automatic firmware updates can be carried out with just a mouse click
- The operator can release his own web addresses (e.g. for the website of his hotel, cafe, club, etc.).
- A so-called “traffic shaping” ensures that uploads do not “clog up” the DSL
Can I continue using my DSL connection properly?
Yes, nothing changes for the hotspot operator. The DSL connection remains unchanged and can be used as usual.
The hotspot has a firewall running on it that can prevent hotspot users from accessing your private network. In addition, VPN routing can be activated, which tunnels the data from the hotspot router through your private network to a VPN server of HOTSPLOTS.
If you want a separate DSL connection for the hotspot, you can also get one from us. Please contact our sales department.
Features of the hotspot router firmware
- Gateway with captive portal. On LAN ports the captive portal is optional.
- Three options for WAN connection: pppoe, static, dynamic/DHCP
- Configuration as hotspot router or repeater
- Packet secure port forwarding (PSPF). I.e. the WLAN clients do not see each other. (This security feature can be deactivated if unwanted.)
- Configuration of transmitter power
- Walled garden: List of domains that can be accessed without authentication and whose traffic is not charged.
- Wireless encryption with openVPN.
- Traffic shaping
- Comfortable graphical user interface
- Configuration of all network settings
- Input and test of HOTSPLOTS operator data
- Download OpenVPN certificate from the HOTSPLOTS server with just a mouse click
- Download and installation of new firmware versions by mouse click
- Activation/deactivation of SSH as an alternative administration tool
- Activation/deactivation of administration by WLAN, LAN and WAN ports
- Change passwords
Which ports must be allowed at a firewall to the internet?
All connections are initiated by the hotspot router. For stateful firewall it is therefore not necessary to open or forward any ports.
For manually configured firewalls it might be necessary to allow certain ports. The following ports are relevant for hotspot-routers:
- DNS:UDP Port 53
- Web: TCP Ports 80, 443
- NTP: UDP Port 123
- VPN-Routing: UDP Ports 1193, 1194, 1195
- HSVPN-Routing: UDP Port 2001
- Radius: UDP Ports 1812, 1813
- Load-Balancing: TCP Ports 5001-5008 (Appliances up to version p6.5), UDP Port 2001 (Appliances with version d8.0 or higher)
With which internet connections does Hotsplots work?
The provider or respectively the medium hardly plays a role here as long as our systems get access to the internet. However, one must be aware that shared internet lines (shared medium) such as cable networks or LTE do not guarantee bandwidth and therefore offer lower throughput in core hours. You can usually find details on this in the general terms and conditions of the internet provider.




